Segmentation
The products of many companies are characterized by a high number of variants with low to medium quantities. The aim of segmentation of a production and assembly is to reduce the complexity of the variety of variants and structure them into suitable units. This requires an examination of the product assemblies (e.g. by breaking down the parts list) as well as the assembly and production sequence. A suitable tool for this would be the assembly priority graph or the routing.
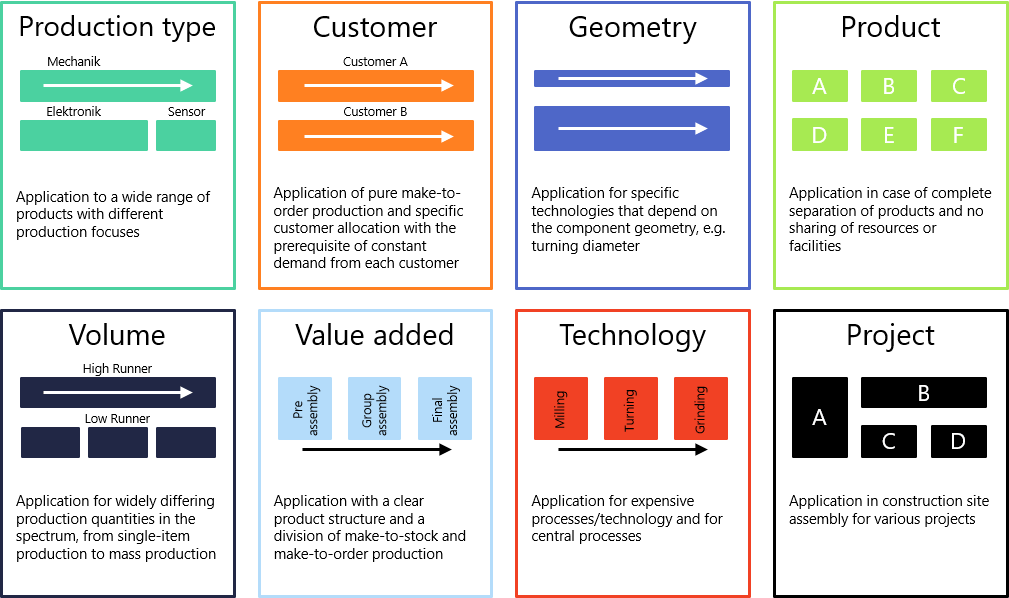
What types of assembly and production segmentation are there?
In principle, 8 types of segmentation for production and assembly can be distinguished using the procedure described above:
- Type of production: Application for a wide range of different products with different production focuses
- Customer: Application of pure contract manufacturing and specific customer allocation with the prerequisite of constant demand from each customer
- Geometry: Application for specific technologies that are dependent on the component geometry, e.g. turning diameter
- Product: Application with complete separation of products and no sharing of resources or facilities
- Quantity: Application for widely varying production quantities in the spectrum, from individual production to mass production
- Value creation: Application with a clear product structure and a division of stock and customer order production
- Process: Application for expensive processes/technology and centralized processes
- Project: Application in construction site assembly for various projects
