
State-of-the-art assembly planning
More flexibility and efficiency with our assembly planning
Assembly planning where every move is perfect
The aim of our consulting and assembly planning is to assign a series of tasks that have to be carried out on the workpiece to a sequence of workstations. Each task requires a specific task duration for its completion. The assignment of tasks to stations is usually done by assembly priority graphs, which indicate which tasks must be completed before a particular task can be started. In addition, scheduling is limited by a cycle time that restricts the sum of task durations that can be completed at each workstation before the workpiece is moved from the conveyor to the next station. Key planning issues in assembly line operations include supply chain integration, inventory control and production planning.
Current trends in assembly
Our assembly planning focuses on making assembly processes more flexible, adaptable and agile in order to cope with increasing product diversity and market volatility. This requirement affects equipment, personnel, production organization and decision-making processes. For example, product customization shifts product identification, i.e. the assignment of a specific workpiece to a specific customer order, earlier in the production process. One reason why it is difficult for manufacturers to fill both skilled and unskilled positions is the lack of vocational training opportunities for young men and women. To solve this problem, many manufacturers are developing robust apprenticeship programs to teach candidates everything from toolmaking and welding to robot programming and plate rolling.
Do you need support with planning your installation?
Our assembly planning is carried out in compliance with established standards such as VDI 6026 and in line with the state of the art. This allows you to remain competitive and easily cope with increasing product diversity and market volatility.
Mounting system – getting the most out of it
In many companies, assembly is the core business. It must be efficient and must not generate costs that can be equated with waste. To achieve this, assembly planning is important to ensure methods for structuring and designing processes within an assembly system and the assembly line. The aim of assembly planning is to keep assembly unit costs as low as possible. This is the only way a company can become or remain competitive in the long term. The focus should include the following points:
- Flexible system in terms of product and extensions
- Reusability of the system thanks to standardized parts for subsequent use
- Use of standardized parts and modular principles
- Reduction of assembly costs in the areas of personnel and investments
- Planning of parts ordering and parts supply
- Achieving the planned number of units in a short time
The 5 steps of assembly planning
Assembly planning has a fixed structure irrespective of the respective products. The most important points are
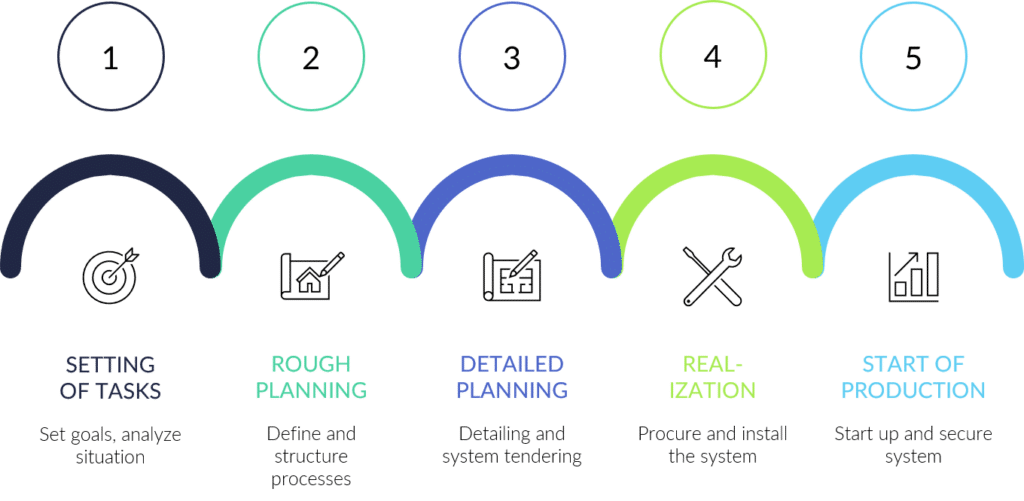
1. Task
This is where goals are set, a situation analysis is carried out, tasks are defined and the time required for the project is determined.
2. Rough planning
Work processes are defined and the assembly structure is developed by segmentation, the necessary hall space is determined, the personnel requirements are planned and the project costing and profitability calculation are carried out.
3. Detailed planning
The overall system is worked out in detail, a schedule is drawn up, the invitation to tender is issued, the deployment of personnel is planned and the economic efficiency is verified.
4. Realization
In this step, the procurement is arranged, the workstations are designed, the personnel are trained, the assembly system is installed and the documentation is created. Testing also takes place.
5. Production start-up
The system start-up is analyzed, errors are eliminated, the documentation is corrected and acceptance is carried out.
