Material supply
The aim of material supply is to increase productivity through transparent processes, low control effort, low circulating stocks and high parts availability through reliable processes.
What types of material provision are there?
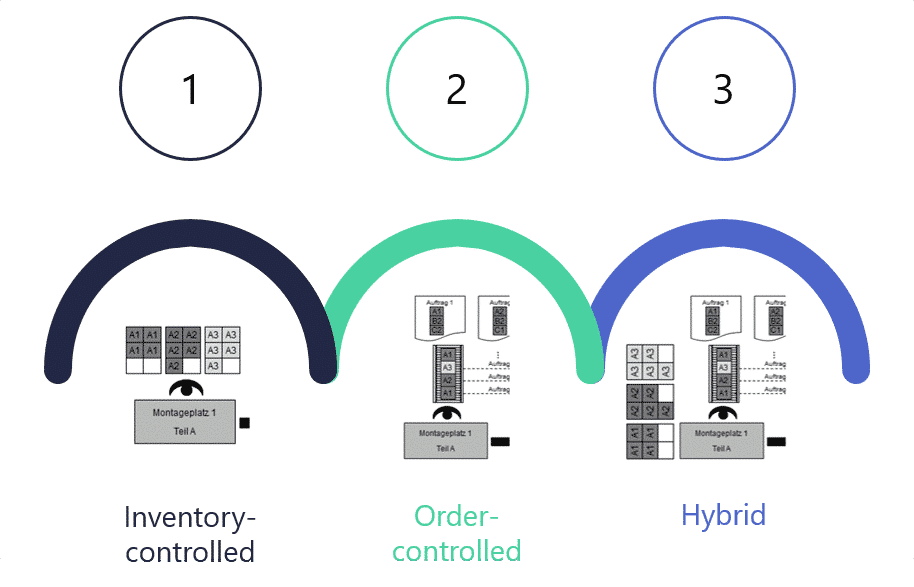
A basic distinction can be made between three types of material provision:
- Inventory-controlled
Provision of all required parts at the workplace for all variants, replenishment of the supply shelves by logistics specialists - Demand-driven
Complete pre-picking of orders by a logistics specialist. “Sequential” provision at the workplace - Mixed form
Provision of identical and C-parts, pre-picking of certain parts of the orders by a logistics specialist, “sequential” provision at the workplace
How do you go about planning the provision of materials?
- Segmenting the material flow to optimize material supply is the first step in planning material provision and logistics. The first step is to identify the different types of parts and to design the logistics processes for the different types in a standardized way to ensure a high level of transparency. The focus is on the lowest possible effort through a high level of standardization for the logistics provider.
- Based on a product analysis, the parts or subsets to be provided are identified and the subsets are broken down into sub-subsets. This step must always be carried out if the individual parts combined in a parts set for material supply are not kept in stock in the same warehouse. The required staging processes are derived and a specific staging strategy is assigned for each parts set or individual part identified.
- The final step is the calculation of the parameters associated with the strategy, such as resource requirements, buffer stock or staging frequency. The second, short-term oriented level of material staging control includes the function of triggering material staging and the short-term adjustment of the staging strategy. These activities are supported by an assembly control station, which fulfills the functions of order coordination and material management in equal measure.

Success factor container management
A further step is container planning and provision at the workplace. The selection of staging principles (container-oriented, order-picked, etc.) and the structure of a container system through to the allocation of parts to containers and the design and dimensioning of staging systems (racks, trolleys, etc.). In order to ensure that the productivity potential gained in assembly is not offset by increased logistics costs, the focus is always on the compromise between assembly efficiency and logistics costs. This is the only way to achieve an overall optimum.
The customer’s standard container sizes can be optimized to minimize the space required for the provision of materials. For example, the provision of B-parts and C-parts on pallets can be replaced by provision in KLTs. Here, too, an appropriate compromise must be found between container sizes and logistics costs. Provision at the workstation aims to minimize gripping distances and optimize ergonomics. Frequently required parts should be staged in the immediate vicinity of the workstation (possibly at flex stations in the case of a large number of variants), and unnecessary bodily twisting and walking by the worker should be avoided.
Efficient material provision
Contact us for a free initial consultation and find out how you too can make your material provision more efficient.
