Künstliche Intelligenz (KI) -Anwendung und Beispiele
The topic of artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming more present every day in all areas of business, industry, education and private life. Not a day goes by without us knowingly or unknowingly relying on the power of AI algorithms. This article presents the most rudimentary basics of artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning.
Artificial intelligence in our everyday lives
People who are not closely involved with AI technology, either professionally or privately, have a vague idea of it. This is mainly inspired by popular science fiction films such as “Terminator”, “Matrix” or “A.I. Artificial lntelligence”. However, today AI is present in far less spectacular and humanoid forms such as spam filters or digital voice assistants like “Alexa” (Amazon) or “Siri” (Apple) and is an essential part of everyday life. For example, AI algorithms are hidden behind every Google query, filtering and categorically presenting the most suitable hits from the almost infinite flow of information on the internet. Spam filters are another example of the use of AI algorithms that make our everyday lives easier.
However, there are also AI applications that sometimes achieve astonishing, but also fatal results, meaning that the general acceptance of the use of AI algorithms to solve problems in society and by authorities is not necessarily there yet. The ongoing digitalization of all branches of industry, combined with the steadily falling costs of data processing and storage, are paving the way for AI in a variety of ways from an academic subject to everyday private and professional life. In the medium term, AI algorithms will become an integral part of our daily lives in the same way as spam filters due to the intensification of research and the increasing volume of data. Specific examples of this vision include autonomous driving of vehicles or sustainable and optimized smart cities, which function in particular using AI algorithms known as deep learning (DL).
The development of AI
AI is a rapidly growing technology that has now found its way into almost all industries worldwide and is expected to bring about a new revolution due to its data processing capabilities.
The term artificial intelligence is an overarching concept that was first introduced at a conference at Dartmouth University in 1956. The term artificial intelligence is generally understood to mean the autonomous assumption and processing of tasks by machines through the development and application of algorithms that enable the machine to act intelligently. A very short and concise definition of AI (out of many possible ones) was given by Elaine Rich, who defines AI as follows:
“Artificial intelligence is the study of how to get computers to do things that humans are currently better at.”
AI is used as a generic term for all developments in computer science that are primarily concerned with the automation of intelligent and emergent behavior such as visual perception, speech recognition, language translation and decision making. Over the past 80 years, a number of sub-areas of AI have emerged. For production and logistics, this primarily concerned machine learning, which initially focused on pattern recognition and later on deep learning using only artificial neural networks. Models and algorithms are essential building blocks for the application of AI to practical problems. An algorithm is defined as follows: It is a set of unique rules given to an AI program to help it learn autonomously from experience (here: data) for a given task (here: the problem under investigation) under a performance measure (here: the error between Kl prediction and a known ground truth within the dataset). The experience is an entire data set consisting of data points (also called examples). A single data point consists at least of features (single measurable property; explanatory variable).
Targets (dependent variables) can also be assigned to the features for specific tasks. The simplest example of this is a regression task where the task for an Al algorithm is to find optimal model parameters given experience, e.g. using the least-squares performance measure.
Machine Learning
Two different main tasks can be distinguished for machine learning, which are briefly presented here. While supervised learning involves developing a predictive model based on both influence and response variables, unsupervised learning involves training a model based only on the influence variables (clustering). In supervised learning, a distinction is also made between classification and regression problems. While in the former the response variables can only assume discrete values, in regression problems the response variables are continuous.
Deep Learning
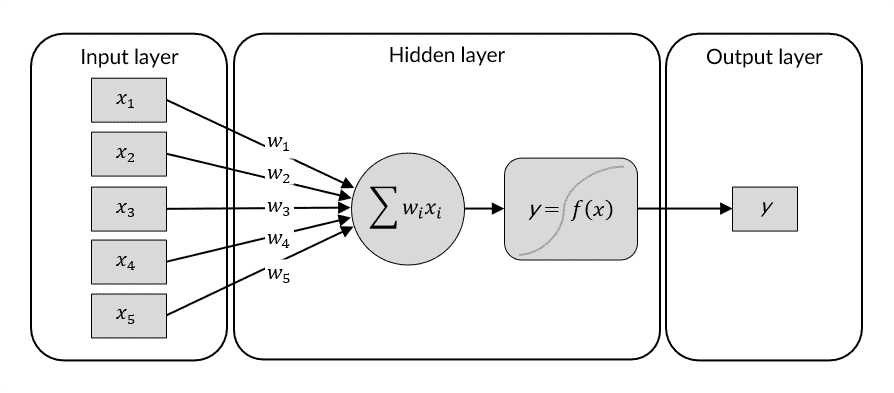
Deep learning uses artificial neural networks (ANN) to recognize patterns and highly non-linear relationships in data. An artificial neural network is based on a collection of connected nodes that resemble the human brain. Due to their ability to reproduce and model non-linear processes, artificial neural networks have found applications in many areas, such as material modeling and development, system identification and control (vehicle control, process control), pattern recognition (radar systems, face recognition, signal classification, object recognition and more). Sequence recognition (gesture, speech, handwriting and text recognition). A CNN is built by connecting layers consisting of multiple neurons, where the first layer of the CNN is the input layer, the last layer is the output layer and the layers in between are called hidden layers. If an ANN has more than 3 hidden layers, it is referred to as a deep neural network.
